The crucial role of sealing solutions in preventing chemical leaks
The chemical industry is responsible for transforming raw materials into valuable products and is widely regarded as one of the most important sectors of the economy. The aggressive and hazardous nature of the chemicals involved in these processes requires robust and reliable engineering solutions. Sealing solutions are one of the most important components in ensuring that chemical plants are safe, efficient and environmentally friendly.
The chemical industry is a complex combination of processes and operations that utilize chemistry to manufacture a variety of products. These processes use a wide variety of raw materials to produce a wide range of primary, secondary and tertiary products. Primary products are the furthest removed from the key users, and demand is often obscure, as each product passes from one process to the next before appearing on the market.
In general, the chemical industry is divided into the following areas:
-
Basic Chemicals
Fine Chemicals
Specialty Chemicals
Inorganic chemicals
Organic Chemicals
Each area of the production process requires unique assets and applications to withstand the aggressive nature of the raw materials as they are transferred from one state to another (see Figure 1), thus requiring the specialized development of sealing solutions.
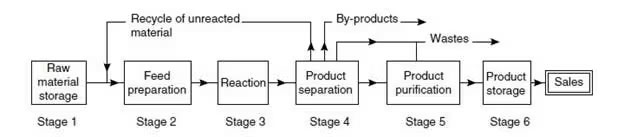
PTFE gaskets are often a reliable choice for sealing in chemical processes.
The Importance of Sealing
Seals play a pivotal role in chemical processing. By preventing the leakage of liquids, gases and other materials, seals ensure that no harmful substances can seep into the production process or have a negative impact on the surrounding environment.
In addition to safety, seals are critical to safeguarding process efficiency. They help regulate key parameters such as pressure, temperature and flow rate, which directly affect the consistency and quality of the production process. Seals ensure optimal operating conditions, increasing productivity and reducing operating costs. In addition, as a protective barrier, sealing solutions significantly extend equipment life, minimize wear and tear, and reduce the need for frequent maintenance or replacement, ultimately leading to long-term cost savings and increased operational reliability.
Seal type and material selection
Therefore, the chemical compatibility of the seal with the system fluid is critical to achieving reliable and durable sealing performance. Because the polymers and other raw materials used in seals vary widely in the way they react with chemicals in the fluid, the selection process can be extremely challenging, especially when relying solely on chemical compatibility charts.
For example, when a particular chemical interacts with certain materials, the chemical can “attack” the polymer bonds, thereby reducing the performance of the polymer. In some cases, the chemical precipitates components from the polymer, thereby weakening the polymer or stripping it of its essential mechanical properties. Other chemicals may penetrate the polymer, causing it to swell. Depending on the application, this swelling may be beneficial or detrimental. In some cases, the media may not affect the polymer at all. Rather, it may have a negative effect on one of the other raw materials used in the sealing material, leading to reduced mechanical properties and potential failure.
The wide variety of processes and chemical media used in the chemical industry means that there is no “one size fits all” option when it comes to sealing. Most chemical plants utilize a variety of sealing solutions. These include.
- elastomer :Made from a variety of different polymers such as Nitrile Rubber (NBR), Ethylene-Propylene-Dimethylene Rubber (EPDM), Silicone, Neoprene, Fluorocarbon Rubber (FKM), etc.; these seals can be used in a variety of applications in the form of gaskets, O-rings and specialty molded seals.
- Compression Fiber:These materials consist of combinations of elastic binders, synthetic, organic and/or inorganic fibers, and other ingredients, and are commonly used in a variety of general-purpose services.
- Flexible graphite :Graphite seals are chemically expanded into rolls or sheets that offer excellent chemical resistance while withstanding higher temperatures than rubber seals. Many graphite seals also feature a metal reinforcement, making them even stronger and able to withstand higher working pressures.
- PTFE:PTFE is probably the most commonly used material for chemical process sealing solutions, providing excellent chemical resistance even in the most aggressive media.
- metals :Metal-based sealing solutions are more common in applications with extremely high temperatures and pressures, but still have their place in chemical processing plants. These seals are made entirely of metal, or a combination of a metal carrier element and a softer sealing element such as graphite or PTFE, and are used to some extent in virtually all industrial manufacturing plants around the world.
Pros and Cons
There are many options for sealing solutions, and choosing the one best suited for a particular application can be challenging. Safety is critical as many of the raw materials used in chemical processing facilities are aggressive and have low tolerance. The ideal solution should provide safe and reliable sealing performance throughout the process until the next scheduled maintenance. Working closely with an experienced manufacturer or supplier of sealing products can be a valuable asset to any chemical plant.
In general, it is important to remember that each sealing solution has its own advantages and disadvantages. For example, elastomeric seals can form a seal at lower loads than most other seals. They are also relatively inexpensive. That's great, right? Well, don't jump to conclusions either. They can be crushed at lower loads than other seals, degrade faster over time (especially at elevated temperatures), and exhibit a high degree of relaxation, which means they don't hold loads as well. Depending on the polymer, their compatibility with various media varies greatly.
On the other hand, PTFE-based seals can withstand some of the most aggressive chemicals on the planet. They are often considered to be flexible materials that adapt well to flange imperfections and have an indefinite shelf life. These are great qualities and characteristics. The main disadvantages of PTFE seals are their higher cost and the fact that in its raw form PTFE is highly susceptible to creep relaxation.
Choosing the right sealing solution for an application requires careful consideration of many of these variables. Sometimes, rubber seals are the right choice. Sometimes a graphite plate, compressed fiber plate or PTFE plate may be the right choice.
Hydrofluoric Acid Production Insight - Case Study
The production of hydrogen fluoride is probably one of the most dangerous and aggressive processes in chemical processing. If incompatible materials react, it can lead to corrosion, weakened mechanical properties and other undesirable interactions. For this reason, a great deal of time must be spent studying not only the sealing materials, but also the seals themselves. For example, deciding which type of sealing gasket to use in hydrogen fluoride production requires careful consideration.
Although HF production process units are closely monitored, unexpected problems can occur. Water introduced during cleaning or maintenance activities and remaining in the system, or leakage intrusion from other parts of the production process, can lead to the formation of hydrofluoric acid, which in turn can lead to corrosion and ultimately to a dangerous leak. Areas of the process where pooling may occur are most susceptible to acid corrosion. As a result, seals that do not fill gaps can lead to corrosion of flanges and sealing surfaces.
In order to accurately and adequately address the challenges of sealing in hydrofluoric acid applications, manufacturers have designed unique sealing technologies. Semi-metallic technology is utilized to create tandem seals with different packings and facings to take advantage of their different strengths. In this application, there are design differences between the type of metal construction used for the primary seal (spiral wound, solid metal with serrations, corrugated metal, etc.). Regardless of the form of construction chosen, it is highly recommended that high temperature, oxidation-resistant grades of flexible graphite be specified as the primary seal material because of its tight sealing properties.
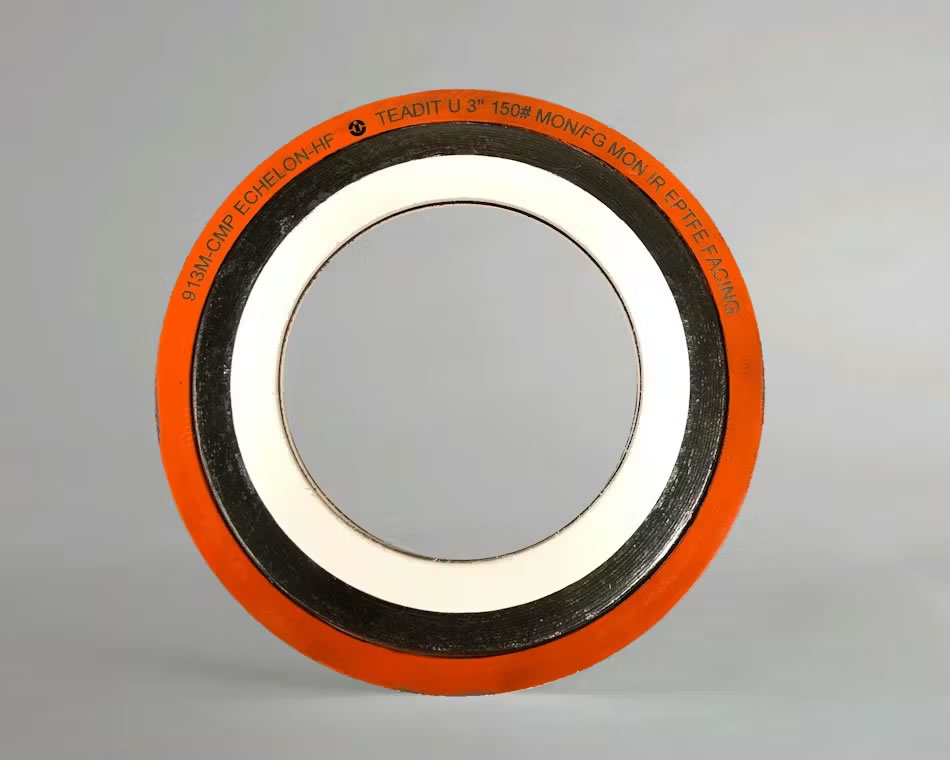

Specialized gaskets for hydrofluoric acid service typically utilize expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) as a secondary sealing element. PTFE is favored in harsh environments because of its almost universal chemical resistance. ePTFE has excellent compressibility, allowing it to fit easily against flange surfaces that may be worn or corroded, completely filling and eliminating gaps. There are many variations in design for secondary sealing, including thickness, core type and method of adhesion. When selecting expanded PTFE for secondary sealing, it is critical to specify a low creep material with uniform density.
The challenge of sealing solutions
Understanding which sealing solution provides the best seal can avoid costly downtime, reduce maintenance requirements, and extend the life of equipment, making it an important investment for any chemical processing facility. Addressing these challenges requires a combination of materials science, engineering expertise and regular maintenance practices:
Material selection: Choosing the right material is critical. Seals made of PTFE or other specialty elastomers are often chemically compatible and can withstand a wide range of chemicals. High temperature applications may require materials such as graphite or metal seals.
Advanced design: Modern seals are designed to accommodate the specialized conditions of chemical processing environments. This includes the use of composite materials, special coatings and advanced geometries to improve sealing performance and durability.
Regular maintenance and monitoring: Implementing a proactive maintenance program can help identify wear before it leads to failure. Periodic inspections, performance monitoring and seal replacement can be included as part of a routine maintenance program.
Customized solutions: In some situations, such as the case of hydrofluoric acid production, standard seals may not be adequate. Custom-designed seals can be tailored to meet the specific requirements of the chemical process, ensuring optimum performance and longevity.
Training and education: Ensuring that plant personnel are adequately trained to install, maintain and replace seals can prevent many common problems. Experienced operators can recognize potential problems early and take corrective action before seals fail.
Sealing solutions are important in complex and demanding chemical processing environments, where they are critical to the safety, efficiency and success of manufacturing operations. By understanding their challenges and utilizing the right materials, design and maintenance practices, chemical plants can ensure effective seal performance to protect their operations and the environment.
作者:TEADIT泰迪集團(tuán) Angelica Pajkovic 與 Chris Morris
原文鏈接:
https://teadit.com/us/article/the-crucial-role-of-sealing-solutions-in-preventing-chemical-leaks/
